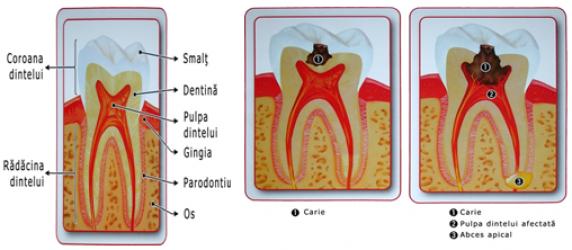
Cavities
Dental decay is a non-inflammatory, chronic destructive process of hard tissues of the tooth causing necrosis and can be followed by a crown or root cavity. Decay develops only on contact with the teeth and partially isolated teeth.
It is considered that the factors involved in decay, are placed in three main groups:
- cariogenic oral microflora;
- fermentable food substrate;
- favorable land (quality enamel and oral fluid)
1. Plaque is a microbial organic compound with intense metabolic activity well adapted to its environment. It appears as an aggregate of organisms linked together and the teeth or other structures in the mouth.
2. Contemporary schools of thought indicate that nutrition has a significant effect on tooth decay, cardiovascular disease, obesity and diabetes, his balance in terms of ratios of power principles is an important preventive factor.
3. Enamel resistance to cavity is largely conditional on enamel structure. Enamel structure is a result of tooth growth during its developmental period and on the other influences exogenous and endogenous performed on adult teeth.